Skeletal muscles attached to the arms, legs, neck, back, and trunk bones are voluntary and consciously controlled. Weakness or inability to control these muscles can signal a health issue like a neuromuscular disorder or electrolyte imbalance. Can recognizing the symptoms can help healthcare providers develop effective treatment programs?
Voluntary Muscles
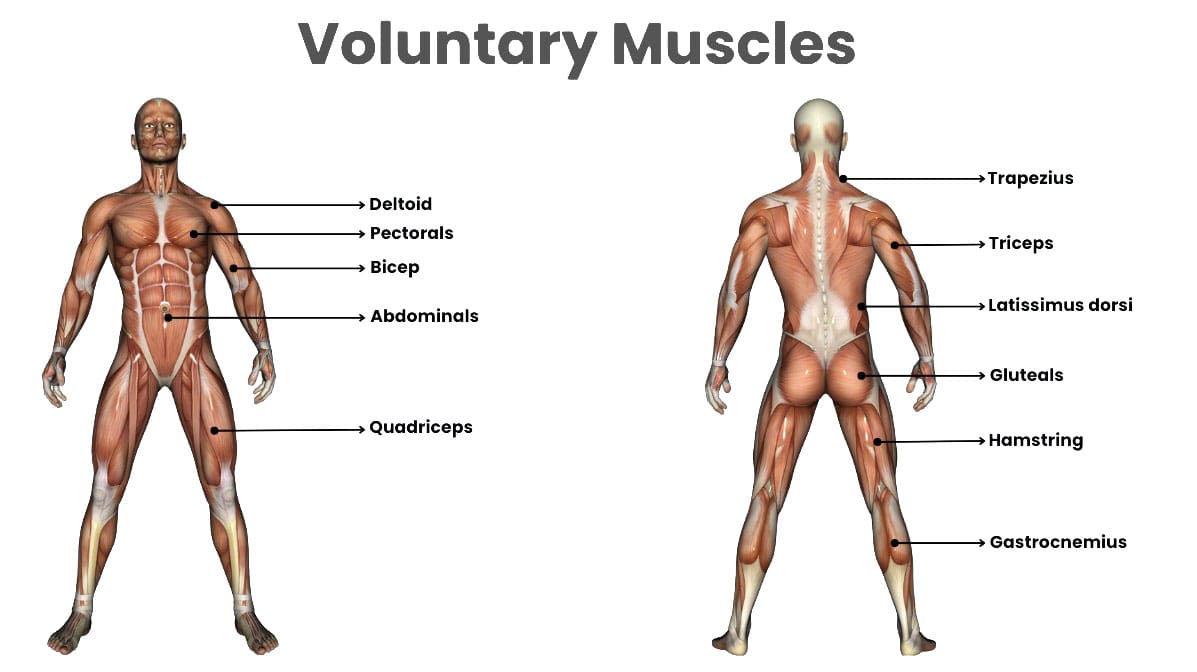
Voluntary muscles are the skeletal muscles that attach to bones and control movement of the limbs, head, neck, and body under an individual’s conscious control. Skeletal muscles are controlled by neuromuscular signals from the brain that communicate with individual muscle fibers and cause them to contract.
Difference
- Voluntary muscles are skeletal muscles that contract and relax under conscious control.
- These muscles attach to bones and regulate movement of the body.
- Involuntary muscles are not under conscious control.
- Involuntary muscles involve automatic internal processes needed for survival, like controlling blood vessels and organs like the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
- They contract and relax automatically and receive signals from the autonomic nervous system, which regulates internal bodily functions.
Voluntary
Voluntary muscles are skeletal muscles that comprise 40% of the body’s weight and 50% to 75% of the body’s proteins. These muscles can convert chemical and mechanical energy to cause voluntary muscle contraction and movement. (Trovato F.M. et al., 2016) Skeletal muscle comprises fascicles or bundled units of multiple muscle fibers or muscle cells. Each muscle fiber consists of a cross-banded structure further divided into myofibrils containing thick myosin and thin actin myofilaments, which give the muscle its stripe appearance, and the structure gives the characteristic striated structure. (Trovato F.M. et al., 2016) Muscle contraction occurs when these myofilaments move closer together, stimulated by the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from nerve cells that communicate with the muscle fiber.
Involuntary
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary muscles, regulating their contraction and relaxation. This system also controls the activity of organs and blood vessels for essential daily functions, including breathing, circulation, digestion, heartbeat regulation, and urination. Most involuntary muscles are composed of smooth muscles. Smooth muscles do not have the striated structure of skeletal muscles and consist of sheets or layers of smooth muscle cells. When the autonomic nervous system stimulates these muscle cells to contract by releasing hormones or other chemical signals, smooth muscle cells shorten through the movement of actin and myosin myofilaments. Involuntary smooth muscles include the blood vessel walls, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder. (Webb R. C. 2003) One exception of an involuntary muscle is the myocardium, or heart muscle. The myocardium comprises a specialized cardiac muscle cell found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle is striated like skeletal muscle but is controlled by the autonomic nervous system and pacemaker cells, causing it to contract automatically and rhythmically.
Weakened Voluntary Muscles
Skeletal muscle diseases, neuromuscular disorders, and other causes can weaken muscles. Neuromuscular or skeletal muscle disorders affect the nerves that send electrical signals to voluntary skeletal muscles to control movement. When the nerves are damaged, communication between the nerves and muscles becomes disrupted. This can result in significant muscle weakness, atrophy, and loss of function. Most neuromuscular disorders are genetic or caused by issues with the immune system. Nerves communicate with muscles through the release of neurotransmitters at the neuromuscular junction, which is the space between a nerve cell and muscle fiber. Neuromuscular disorders can damage the nerve or the neuromuscular junction. Neuromuscular disorder symptoms can include: (Cleveland Clinic, 2023)
- Numbness and tingling
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle twitches, cramps, or spasms
- Muscle pain
- Muscle atrophy
- Decreased coordination
- Balance problems
- Drooping eyelids and double vision from eye muscle weakness.
- Difficulty swallowing due to weakness of the pharynx.
- Difficulty breathing due to weakness of the diaphragm.
Common Neuromuscular Disorders
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis – ALS
- More commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, it is a genetic disorder that results from hardening of the spinal cord.
- It causes damage to the nerves that control muscles and voluntary movement.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
- This is a class of peripheral nerve disorders that cause muscle weakness, atrophy, and loss of sensation, most commonly in the legs and feet.
- It is a genetic disorder caused by a gene mutation that damages myelin, or the insulating sheath that surrounds all nerves and supports the conduction of electrical signals.
Multiple Sclerosis – MS
- MS causes degeneration of the myelin sheath surrounding nerves, decreasing the impulses along the nerves to muscles.
- It can result in muscle weakness, which is often more severe on the dominant side of the body.
- There are different forms of MS, but the condition is often progressive and gets worse over time if left untreated.
Muscular Dystrophies
- These are genetic diseases characterized by gradual loss of motor function, muscle weakness and atrophy, walking gait problems, progressive respiratory failure, and cardiomyopathy.
- There are nine types of muscular dystrophy, all caused by genetic mutations.
Myasthenia Gravis
- This is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation throughout the body.
- An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system attacks healthy cells by mistake.
- With myasthenia gravis, the body produces antibodies that attack the receptors for acetylcholine, reducing the body’s ability to contract muscles.
- This leads to muscle weakness, atrophy, and fatigue.
Myopathies
- These are diseases of muscles that cause muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Depending on the type, they may progress and get worse over time.
Electrolyte Imbalances
- Muscle weakness can result from altered sodium, potassium, calcium, or magnesium levels.
Always seek immediate medical attention for any sudden, unexplained muscle weakness. Individuals who experience skeletal muscle weakness should discuss the type and duration of symptoms with their doctor, specialist, physical therapist, or chiropractor, as this might be a sign of a medical condition such as a neuromuscular disorder. Working with a chiropractic team can help expedite healing. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic works with primary healthcare providers and specialists to develop a personalized treatment program through an integrated approach to treat injuries and chronic pain syndromes, improving flexibility, mobility, and agility, relieving pain, and helping individuals return to normal activities. If other treatments are needed, Dr. Jimenez has teamed up with top surgeons, clinical specialists, medical researchers, and rehabilitation providers to provide the most effective treatments.
Chiropractic Massage Therapy
References
Trovato FM, I. M., Conway N, Castrogiovanni P. (2016). Morphological and functional aspects of human skeletal muscle. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol., 1(3), 289-302. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk1030289
Webb R. C. (2003). Smooth muscle contraction and relaxation. Advances in physiology education, 27(1-4), 201–206. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.00025.2003
Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Mitochondrial diseases. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15612-mitochondrial-diseases
Post Disclaimer *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Voluntary Muscles: A Closer Look at Skeletal Muscle Control" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Fitness, Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Verify Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics



