How is fat turned into energy to be used as fuel for individuals working to improve their health and physical abilities?
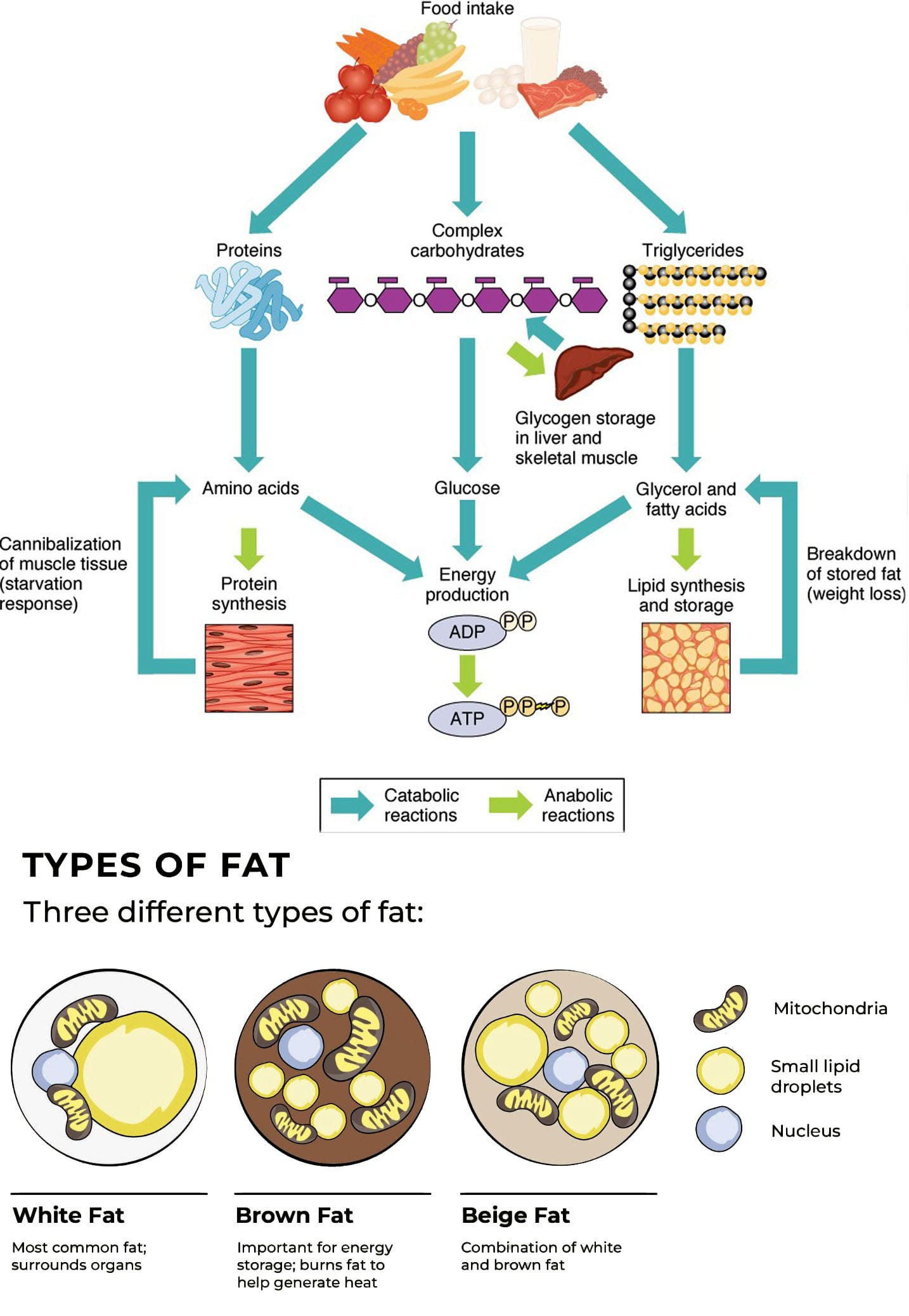
Fat Into Energy Conversion
Fat is an essential component of a diet that fuels physical activity, work, exercise, etc. Its calorie density is the highest of all nutrients, and fat’s unlimited storage capacity makes it the body’s largest energy reserve. Fat is essential for longer, slower, lower-intensity endurance physical activities and exercises like walking and cycling.
What Is Fat?
Everything eaten is made up of:
Macronutrients
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- Fat
Micronutrients
- Vitamins
- Minerals
These are converted to energy, helping to fuel all bodily functions.
Dietary fat has been blamed for various health problems, but it is an essential nutrient for optimal health. The adipose tissue/stored fat provides cushion and insulation to internal organs, protects nerves, circulates vitamins A, D, E, and K through the body, and is the largest stored energy reserve. Stored body fat is different from dietary fat. Body fat is only stored when more calories are consumed than used from all foods, not just from dietary fats. There is an optimal level of body fat for health and regular physical and athletic activity.
Types
Researchers and scientists are learning more and more about body fat/adipose tissue and its roles in the body. Two well-known types are white fat and brown fat.
- Brown fat helps regulate body temperature. (Richard AJ. et al., 2020)
- White fat is responsible for energy storage and metabolic functions like insulin sensitivity.
- White fat can transition to brown fat under certain cold temperatures. (Rabiee A. 2020)
- Beige fat is another type that scientists are still learning about.
When Fat Is Burned
When fat is used as fuel, the fatty acids inside the fat cell are broken down and released into the system as water and carbon dioxide. (MacLean P. S. et al., 2015) The body uses the water for hydration, and the carbon dioxide is exhaled through the lungs. The remaining fat cell shrinks as it is depleted of its fatty acids. The fat into energy conversion also produces heat.
Fat for Fuel
Fat is the main fuel source for long-duration, low—to moderate-intensity physical activities and exercise like endurance sports. Even during high-intensity activities and training, where carbohydrates are the main fuel source, the body still needs fat to help access the stored carbohydrates or glycogen. Using fat to fuel activity includes three key components which include:
Digestion
- Fat is slow to digest and convert into a usable form of energy.
- The process can take up to six hours.
Transportation
- After the body breaks down the fat, it needs time to transport it to the working muscles before it can be used as energy.
Conversion
- Converting stored body fat into energy takes increased oxygen, requiring decreased physical activity and exercise intensity.
This is why timing when and how much fat is consumed is important for its full potential. Eating foods high in fat immediately before or during intense physical work activity or exercise is not recommended. First, the job, chore, or workout will be done before the fat can be used as energy. And second, it can cause uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Fat Loss Optimization
For individuals trying to alter body fat composition, the most important thing is to adopt a safe and effective physical activity and exercise routine and to eat a balanced diet of nutrient-dense foods that provide adequate amounts of macronutrients, including dietary fat.
Macronutrient
Low-carbohydrate and high-fat diets, like the ketogenic and Paleo diets, all work on the same premise: Lower carbohydrate intake, high fat intake, and moderate to high protein intake lead to burning body fat as the primary fuel source while engaging in physical activity or exercising. There is some scientific evidence that long-term low-carb/high-fat diets are safe and may help improve metabolic risk factors for chronic disease. Some studies on these diets have shown them to be beneficial for performance in endurance sports, but several months of adaptation to a low-carb/high-fat diet are required for metabolic changes to occur. (Chang C. K., Borer K., and Lin P. J. 2017))
High-Intensity Interval Training
High-intensity interval training is an efficient way to convert fat to energy. In a study, overweight individuals were able to convert body fat to energy in half the time using HIIT vs. aerobic activity alone (Zhang H. et al., 2017). HIIT specifically converts visceral fat, typically white adipose tissue, often found in the midsection. (Mittal B. 2019) HIIT also helps increase muscle mass and resting metabolism. (Thyfault J. P. and Bergouignan A. 2020) However, any exercise regimen that helps increase muscle mass provides these beneficial effects.
Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic
At Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic, we focus on what works for you to relieve pain, restore function, prevent injury, and better the body. Through research methods and total wellness programs, individuals can condition themselves to excel in physical activity or sports through proper fitness and nutrition. Regarding musculoskeletal pain, specialists like chiropractors, acupuncturists, and massage therapists can help mitigate the pain through spinal adjustments that help the body realign itself. They can also work with other medical professionals to integrate a treatment plan to resolve musculoskeletal issues.
Integrative Medicine and Chiropractic Care
References
Richard, A. J., White, U., Elks, C. M., & Stephens, J. M. (2000). Adipose Tissue: Physiology to Metabolic Dysfunction. In K. R. Feingold, B. Anawalt, M. R. Blackman, A. Boyce, G. Chrousos, E. Corpas, W. W. de Herder, K. Dhatariya, K. Dungan, J. Hofland, S. Kalra, G. Kaltsas, N. Kapoor, C. Koch, P. Kopp, M. Korbonits, C. S. Kovacs, W. Kuohung, B. Laferrere, M. Levy, E. A. McGee, R. McLachlan, M. New, J. Purnell, R. Sahay, A. S. Shah, F. Singer, M. A. Sperling, C. A. Stratakis, D. L. Trence, & D. P. Wilson (Eds.), Endotext. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32255578
Rabiee A. (2020). Beige Fat Maintenance; Toward a Sustained Metabolic Health. Frontiers in endocrinology, 11, 634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00634
MacLean, P. S., Higgins, J. A., Giles, E. D., Sherk, V. D., & Jackman, M. R. (2015). The role for adipose tissue in weight regain after weight loss. Obesity reviews : an official journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 16 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), 45–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12255
Chang, C. K., Borer, K., & Lin, P. J. (2017). Low-Carbohydrate-High-Fat Diet: Can it Help Exercise Performance?. Journal of human kinetics, 56, 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1515/hukin-2017-0025
Zhang, H., Tong, T. K., Qiu, W., Zhang, X., Zhou, S., Liu, Y., & He, Y. (2017). Comparable Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training and Prolonged Continuous Exercise Training on Abdominal Visceral Fat Reduction in Obese Young Women. Journal of diabetes research, 2017, 5071740. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5071740
Mittal B. (2019). Subcutaneous adipose tissue & visceral adipose tissue. The Indian journal of medical research, 149(5), 571–573. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1910_18
Thyfault, J. P., & Bergouignan, A. (2020). Exercise and metabolic health: beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia, 63(8), 1464–1474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05177-6
Post Disclaimer *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Turning Fat into Energy: Understanding its Role in the Body" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Fitness, Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Verify Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics



