Introduction
The body relies on the gut system to help regulate its homeostasis and metabolize the nutrients for the immune system. The beneficial gut bacteria help maintain the intestinal walls from developing chronic issues and affecting the entire body. The gut system also provides information to the central nervous system through the spinal cord to the brain. The neuron signals help transport the information to all the corresponding muscles, tissues, and organs that require the gut system to stay healthy and functional. When the gut develops issues, the related muscles, tissues, nerves, and surrounding organs begin to feel the effects, causing the body to be dysfunctional. When this happens, many individuals will start to suffer pain and go to their physicians to find relief. Today’s article focuses on the sympathetic nervous system, how it affects the body, and how gut disorders can disruptively affect the sympathetic nerves in the surrounded torso area. We refer patients to certified, skilled providers specializing in gastrointestinal and chiropractic treatments that help those suffering from gut disorders and bodily pain. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is critical for asking insightful questions to our providers. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
Can my insurance cover it? Yes, it may. If you are uncertain, here is the link to all the insurance providers we cover. If you have any questions or concerns, please call Dr. Jimenez at 915-850-0900.
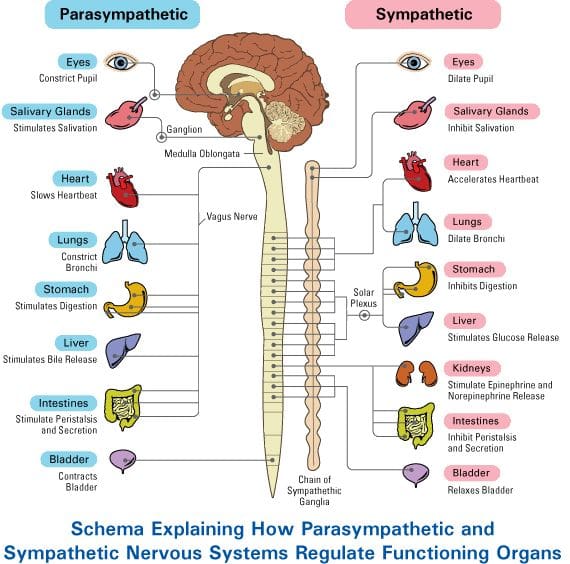
The Sympathetic Nervous System
Have you been feeling stressed throughout the entire day? Do symptoms of inflammation tend to flare around the abdominal area or the abdominal organs? Do your muscles seem to tense up more than they should, even in their relaxed state? All of these signs and symptoms that affect the abdominal region of the body are all connected to the sympathetic nervous system in the body. Research studies have defined the sympathetic nervous system as part of the autonomic nervous system, a central nervous system component. The best way to describe the sympathetic nervous system is that it activates the adrenal glands to produce the hormone adrenaline causing the body to be in a “fight or flight” mode. The sympathetic nerves also help regulate the alpha and beta receptor activity of the various corresponding organs that stimulate the blood vessels surrounding the body, causing a relationship of the organs to the muscles.
How Does It Affect The Body?
As part of the autonomic system, the sympathetic nervous and parasympathetic systems help the body achieve homeostasis by exerting influences over the organ systems. Research studies have shown that this causes the organ systems to upregulate and downregulate the various functions that each muscle needs. Some of the tasks that the sympathetic nervous system that activates these organs include:
- An increased metabolism
- Decreased GI motility
- An increased heart rate
- An increase in movement and strength
- Suppression in the immune system
- Constriction of the large arteries and veins
- Increase glucose production
Additional studies have noticed that the neurons in the sympathetic nervous system help prepare the body for various physical activities that affect the organs. This causal relationship between the organs and muscles helps redirect the blood flow to different body parts. The sensory impulses of the somatic tissue will then correlate to the spinal cord’s thoracic and lumbar spinal regions. When these nerves become irritated, it can coincidently cause a direct overlap on the muscles and visceral organs surrounding the nerves, changing their functionality. This causes somatic dysfunction to create the impression of overlapping profiles affecting the internal organs.
An Overview Of The Sympathetic Nervous System-Video
Have you experienced knee pain while having issues in the pelvic region? How about feeling pain in the lower abdomen that triggers spinal stiffness in the lumbar parts of the back? Or have you noticed any pain from the testicular area is relieved after a spinal manipulation? These symptoms are mediators of the sympathetic nervous system when internal organs are damaged. The video above explains the sympathetic nervous system and how it functions in the body. When the body suffers from traumatic forces or ordinary factors, it can cause an increased risk of other associated problems that can also affect it. The afferent fibers from the sympathetic nervous system can carry the pain signals from the somatic and visceral tissues that converge at the common synaptic site that is within the spinal cord. Research has stated that the somatic nociceptive signals can disrupt the gastrointestinal tract due to stress from various locations in the gut system. When this happens, it can cause an overlap of risk profiles in the entire body.
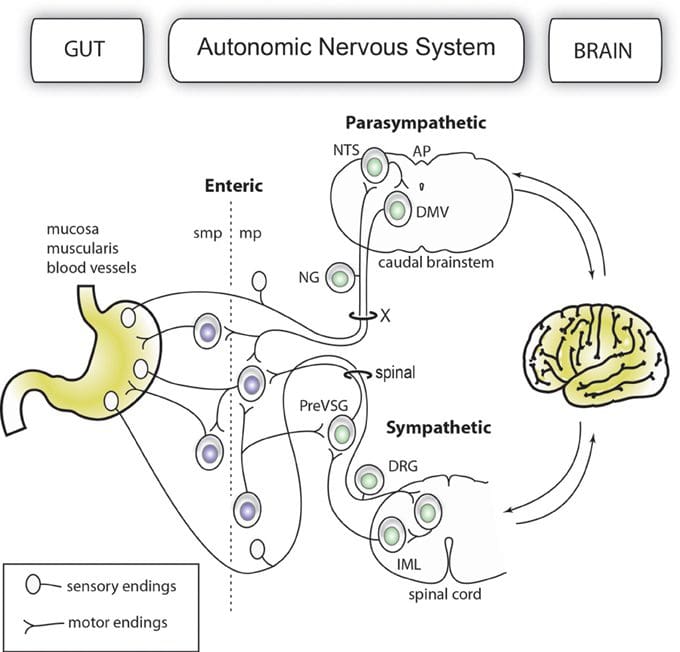
How Do Gut Disorders Affect The Sympathetic Nerves?
The way the gut system works is that it provides homeostasis to the body by regulating the immune system. When the sympathetic nerves are intertwined with the gut system and the spinal cord, research studies show that the sympathetic innervation to the GI tract helps regulate the motility, secretion, and blood flow by correlating to the nervous system’s activity and modulating GI inflammation. When the guts system begins to suffer from disorders affecting the entire body, it can trigger alarm points to the meridians that closely associate with one or more internal organs in the gut system. These alarm points are coincidentally represented as the first instances of visceral pain or tenderness to the somatic structures. When this happens, many physicians will notice that visceral pain involvement overlaps with referred pain, correlating with the individual’s history and other signs of dysfunction. This is a technique called nerve tracing, where physicians follow the line of tenderness from a painful region of the body to the spine, like how GI issues can cause musculoskeletal pain and disturb the visceral tone.
Conclusion
The body requires the gut to maintain homeostasis and help regulate the immune system. The gut system also provides information to the central nervous system by letting the neuron signals transport the sensory-motor functions through the sympathetic nervous system to make the body functional. The sympathetic nerves help provide organ activation to the body that can help prepare the body for various activities. When the sympathetic nerves become irritated, it can cause the muscles and organs to be triggered and change their functionality. This can make the surrounding organs and muscles have an increased risk associated with other disorders that affect the body and correlate to different symptoms. When individuals inform their primary physicians about these symptoms, it gives them a better understanding of these disorders’ causation.
References
Alshask, Mark N, and Joe M Das. “Neuroanatomy, Sympathetic Nervous System.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 14 May 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542195/.
Boezaart, Andre P, et al. “Visceral versus Somatic Pain: An Educational Review of Anatomy and Clinical Implications.” Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine, July 2021, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34145074/.
Cervi, Andrea L, et al. “Neural Regulation of Gastrointestinal Inflammation: Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System.” Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic & Clinical, U.S. National Library of Medicine, May 2014, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24412637/.
LeBouef, Tyler, et al. “Physiology, Autonomic Nervous System.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 8 May 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538516/.
Waxenbaum, Joshua A, et al. “Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System – Statpearls – NCBI Bookshelf.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 29 June 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539845/.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "How Somatic Pain Can Affect The Gastrointestinal Tract" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Fitness, Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Verify Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics