Introduction
The hips in the lower extremities of the body help stabilize the weight of the upper half while providing movement to the lower half. The hips also allow the body to twist, turn, and bend back and forth. The hip joints connect to the inside of the pelvic bone, while the pelvic bone is connected to the sacroiliac joint, which connects to the spine. When natural wear and tear affects the joints as the body ages, issues like hip pain and osteoarthritis associated with low back pain occur, causing various symptoms to arise in the body. Today’s article looks at osteoarthritis, how it impacts the hips, and how to manage hip osteoarthritis. We refer patients to certified providers specializing in musculoskeletal therapies to help those with hip pain and osteoarthritis. We also guide our patients by referring to our associated medical providers based on their examination when it’s appropriate. We find that education is the solution to asking our providers insightful questions. Dr. Alex Jimenez DC provides this information as an educational service only. Disclaimer
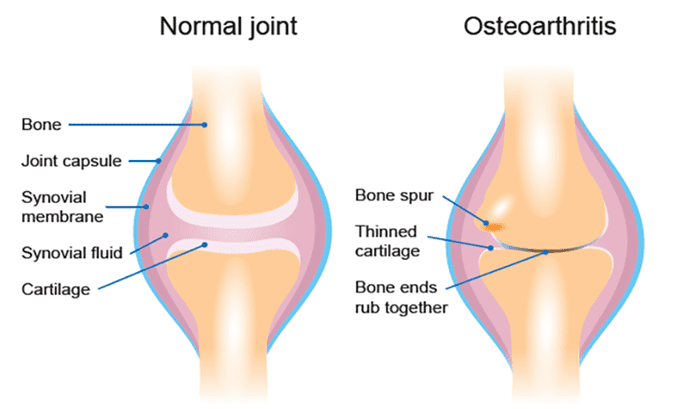
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Have you been experiencing pain in your hips or lower back? How about muscle stiffness near the groin? Do symptoms associated with sciatica seem to flare up near your hips and the back of your leg? Many of these symptoms are signs that you could be at risk of developing osteoarthritis near your hips. While arthritis refers to inflammation of the body’s joints, osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that causes degeneration of the joint cartilage, triggering joint pain and functionality loss. Even though there are several hundred types of arthritis, osteoarthritis is one of the most common types that many people, especially older adults, are affected by. As the body becomes older naturally through age, the repairs from an injury begin to slow down, and the cartilage (the connective tissue that protects the bones from each other) will start to thin out, triggering bone rubbing together, causing inflammation to occur, bone spurs, and inevitable pain. Osteoarthritis is often associated with old age and is multifactorial as factors that can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis include:
- Sex
- Age
- Obesity
- Joint injuries
- Genetics
- Bone deformities
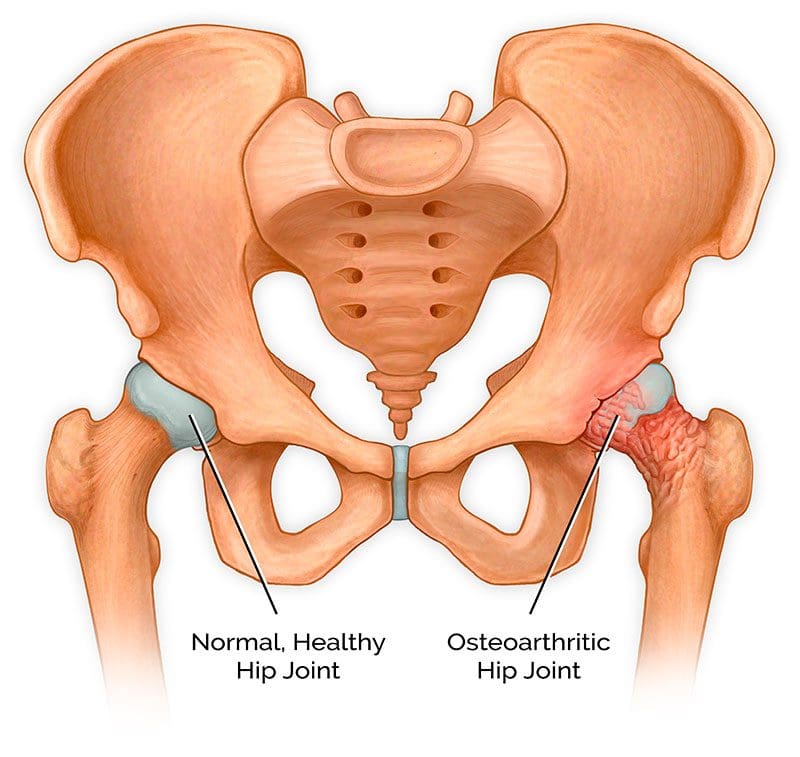
How Does It Impact The Hips?
Since osteoarthritis affects the joints, how does it cause an impact on the hips? When health issues affect the body, it can cause painful symptoms to gradually worsen and become a risk of developing hip pain. Studies reveal that hip pain is common in all adults and activity levels in the anterior, lateral, or posterior regions near the hips.
- Anterior hip pain: Causes referred pain (pain felt in one part of the body but is actually in a different location) associated with internal organ systems.
- Lateral hip pain: Causes wear-and-tear pain on the soft muscle tissues on the sides of the hips.
- Posterior hip pain: Causes referred pain associated with the lumbar spinal pathology like sciatic nerve entrapment correlating with a deep gluteal syndrome.
All these issues affecting the hips overlap with various issues associated with osteoarthritis. When hip pain originates from osteoarthritis, factors like minimal physical activity or slight movements while resting in bed can worsen due to the hip joints having limited or restricted movement. Studies reveal that hip pain is associated with simple movement impairments that make it difficult to diagnose due to referred pain from the spine, knees, or even the groin area.
How does hip osteoarthritis correlate with groin pain? Studies reveal that when a person is dealing with hip osteoarthritis, groin and buttock pain are slightly more common. The hip joint is behind the groin muscle, which is why groin pain overlaps with hip pain as the root. Hip and groin pain could also be involved with radiating pain down toward the knees in the body.
Exercises For Hip Osteoarthritis- Video
Are you experiencing bladder issues? How about stiffness near or around your hips and groin area? Do issues like low back and sciatica pain? Experiencing these issues could be signs of hip osteoarthritis affecting your lower body. Studies reveal that hip osteoarthritis is a significant source of morbidity, pain, gait abnormalities, and functional impairments potentially involved with other issues. Fortunately, there are ways to manage hip osteoarthritis, as the video above shows eight great exercises for hip osteoarthritis. Certain exercise moves for individuals with hip osteoarthritis can help strengthen the surrounding muscles around the joints while increasing joint mobility to reduce pain and stiffness. Exercising can also be beneficial to the individual as it can provide:
- Increase blood circulation
- Maintain weight
- Provides energy boost
- Improves sleep
- Promotes muscle endurance
Other available therapies help manage hip osteoarthritis while alleviating associated symptoms affecting the body.
Managing Hip Osteoarthritis Pain
Many individuals suffering from hip osteoarthritis try to find ways to relieve the pain. While they can’t do anything to prevent wear and tear on the joints completely, there are ways to slow down the process and manage hip osteoarthritis in the body. Small changes like incorporating food can dampen inflammatory effects on the joints while providing nutrients to the body. An exercise regime can help strengthen the weak muscles supporting the joints while increasing mobility and range of motion. Treatments like spinal traction and chiropractic care relieve pain and stiffness from joint disorders like osteoarthritis. Chiropractic care provides spinal manipulation on the back and joints to be adjusted. While spinal traction helps the compressed discs lay off the pressure on the surrounding nerves associated with hip pain. Incorporating any of these can help slow the progression of hip osteoarthritis and bring back mobility to the hips.
Conclusion
The hips provide stability to the upper and lower parts of the body. While supporting the weight of the upper half and movement to the lower half, the hips can succumb to wear and tear in the body. When the hip joints begin to wear and tear slowly, it can lead to the progression of hip osteoarthritis, where the cartilage of the joints begins to cause the bones to rub against each other, triggering inflammation. Hip osteoarthritis makes diagnosing difficult because the referred pain from the spine, knees, or groin area overlaps the symptoms. All is not lost, as there are available treatments to manage hip osteoarthritis that can help slow the progress of this disorder and bring back the mobility of the lower half of the body.
References
Ahuja, Vanita, et al. “Chronic Hip Pain in Adults: Current Knowledge and Future Prospective.” Journal of Anaesthesiology, Clinical Pharmacology, Wolters Kluwer – Medknow, 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8022067/.
Chamberlain, Rachel. “Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis.” American Family Physician, 15 Jan. 2021, https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2021/0115/p81.html.
Khan, A M, et al. “Hip Osteoarthritis: Where Is the Pain?” Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Mar. 2004, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15005931/.
Kim, Chan, et al. “Association of Hip Pain with Radiographic Evidence of Hip Osteoarthritis: Diagnostic Test Study.” BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.), BMJ Publishing Group Ltd., 2 Dec. 2015, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4667842/.
Sen, Rouhin, and John A Hurley. “Osteoarthritis – Statpearls – NCBI Bookshelf.” In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing, 1 May 2022, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482326/.
Disclaimer
Post Disclaimer *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "The Impact On Osteoarthritis On The Hips" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Fitness, Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Verify Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics