Can knowing treatment options for a dislocated hip help individuals expedite rehabilitation and recovery?
Dislocated Hip
A dislocated hip is an uncommon injury but can happen due to trauma or following hip replacement surgery. It usually occurs after severe trauma, including motor vehicle collisions, falls, and sometimes sports injuries. (Caylyne Arnold et al., 2017) A dislocated hip can also occur after hip replacement surgery. Other injuries like ligament tears, cartilage damage, and bone fractures can occur alongside the dislocation. Most hip dislocations are treated with a joint reduction procedure that resets the ball into the socket. It is usually done with sedation or general anesthesia. Rehabilitation takes time and could be a few months before full recovery. Physical therapy can help restore motion and strength in the hip.
What Is It?
If the hip is only partially dislocated, it’s called a hip subluxation. When this happens, the hip joint head only partially emerges from the socket. A dislocated hip is when the head or ball of the joint shifts or pops out of the socket. Because an artificial hip differs from a normal hip joint, the risk of dislocation increases after joint replacement. A study found that around 2% of individuals who undergo total hip replacement will experience hip dislocation within a year, with the cumulative risk increasing by approximately 1% over five years. (Jens Dargel et al., 2014) However, new technological prosthetics and surgical techniques are making this less common.
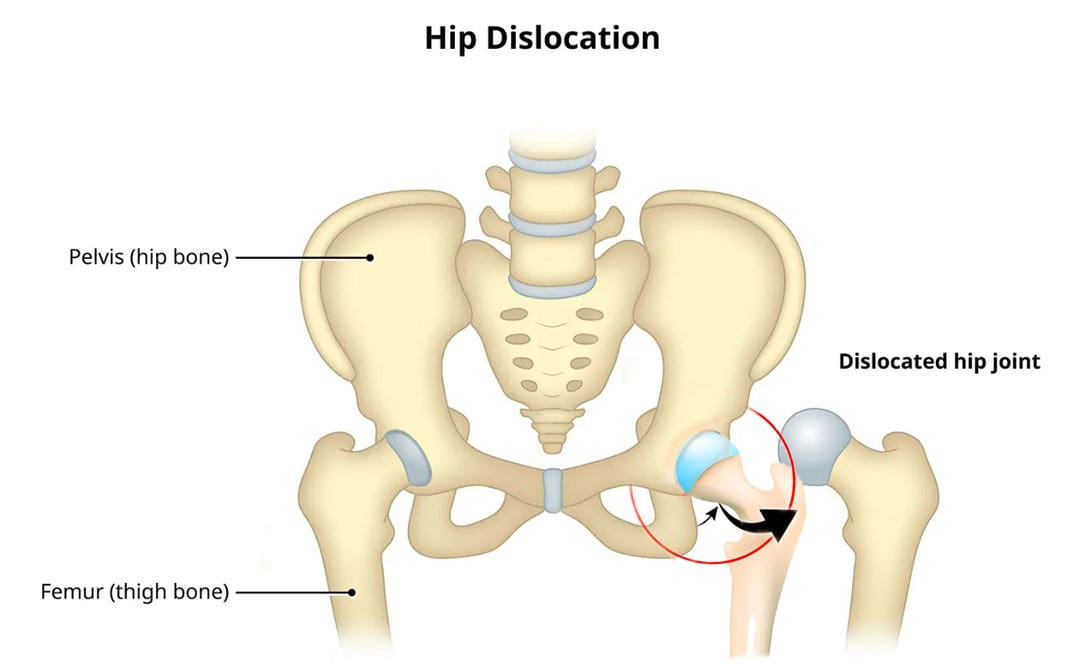
Hip Anatomy
- The hip ball-and-socket joint is called the femoroacetabular joint.
- The socket is called the acetabulum.
- The ball is called the femoral head.
The bony anatomy and strong ligaments, muscles, and tendons help to create a stable joint. Significant force must be applied to the joint for a hip dislocation to occur. Some individuals report feeling a snapping sensation of the hip. This usually is not a hip dislocation but indicates a different disorder known as snapping hip syndrome. (Paul Walker et al., 2021)
Posterior Hip Dislocation
- Around 90% of hip dislocations are posterior.
- In this type, the ball is pushed backward from the socket.
- Posterior dislocations can result in injuries or irritation to the sciatic nerve. (R Cornwall, T E Radomisli 2000)
Anterior Hip Dislocation
- Anterior dislocations are less common.
- In this type of injury, the ball is pushed out of the socket.
Hip Subluxation
- A hip subluxation occurs when the hip joint ball starts to come out of the socket partially.
- Also known as a partial dislocation, it can turn into a fully dislocated hip joint if not allowed to heal properly.
Symptoms
Symptoms can include:
- The leg is in an abnormal position.
- Difficulty moving.
- Severe hip pain.
- Inability to bear weight.
- Mechanical lower back pain can create confusion when making a proper diagnosis.
- With a posterior dislocation, the knee and foot will be rotated towards the body’s midline.
- An anterior dislocation will rotate the knee and foot away from the midline. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2021)
Causes
A dislocation can cause damage to the structures that hold the ball in the socket and can include:
- Cartilage damage to the joint –
- Tears in the labrum and ligaments.
- Fractures of the bone at the joint.
- Injury to the vessels that supply blood can later lead to avascular necrosis or osteonecrosis of the hip. (Patrick Kellam, Robert F. Ostrum 2016)
- A hip dislocation increases the risk of developing joint arthritis following the injury and can raise the risk of needing a hip replacement later in life. (Hsuan-Hsiao Ma et al., 2020)
Developmental Dislocation of the Hip
- Some children are born with developmental dislocation of the hip or DDH.
- Children with DDH have hip joints that did not form correctly during development.
- This causes a loose fit in the socket.
- In some cases, the hip joint is completely dislocated.
- In others, it’s prone to becoming dislocated.
- In milder cases, the joint is loose but not prone to becoming dislocated. (American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. 2022)
Treatment
Joint reduction is the most common way to treat a dislocated hip. The procedure repositions the ball back into the socket and is usually done with sedation or under general anesthesia. Repositioning a hip requires significant force. A hip dislocation is considered an emergency, and reduction should be performed immediately after the dislocation to prevent permanent complications and invasive treatment. (Caylyne Arnold et al., 2017)
- Once the ball is back in the socket, the healthcare provider will look for bone, cartilage, and ligament injuries.
- Depending on what the healthcare provider finds, further treatment may be necessary.
- Fractured or broken bones may need to be repaired to keep the ball within the socket.
- Damaged cartilage may have to be removed.
Surgery
Surgery could be necessary to return the joint to its normal position. Hip arthroscopy can minimize the invasiveness of certain procedures. A surgeon inserts a microscopic camera into the hip joint to help the surgeon repair the injury using instruments inserted through other small incisions.
Hip replacement surgery replaces the ball and socket, a common and successful orthopedic surgical procedure. This surgery may be performed for various reasons, including trauma or arthritis, as it is common to develop early arthritis of the hip after this type of trauma. This is why many who have a dislocation ultimately need hip replacement surgery. As a major surgical procedure, it is not without risks. Possible complications include:
- Infection
- Aseptic loosening (the loosening of the joint without infection)
- Hip dislocation
Recovery
Recovering from a hip dislocation is a long process. Individuals will need to walk with crutches or other devices early in recovery. Physical therapy will improve the range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the hip. Recovery time will depend on whether other injuries, such as fractures or tears, are present. If the hip joint was reduced and there were no other injuries, it may take six to ten weeks to recover to the point where weight can be placed on the leg. It could be between two and three months for a full recovery. Keeping weight off the leg is important until the surgeon or physical therapist gives the all-clear. Injury Medical Chiropractic and Functional Medicine Clinic will work with an individual’s primary healthcare provider and other surgeons or specialists to develop an optimal personalized treatment plan.
Chiropractic Solutions for Osteoarthritis
References
Arnold, C., Fayos, Z., Bruner, D., Arnold, D., Gupta, N., & Nusbaum, J. (2017). Managing dislocations of the hip, knee, and ankle in the emergency department [digest]. Emergency medicine practice, 19(12 Suppl Points & Pearls), 1–2.
Dargel, J., Oppermann, J., Brüggemann, G. P., & Eysel, P. (2014). Dislocation following total hip replacement. Deutsches Arzteblatt international, 111(51-52), 884–890. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2014.0884
Walker, P., Ellis, E., Scofield, J., Kongchum, T., Sherman, W. F., & Kaye, A. D. (2021). Snapping Hip Syndrome: A Comprehensive Update. Orthopedic reviews, 13(2), 25088. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.25088
Cornwall, R., & Radomisli, T. E. (2000). Nerve injury in traumatic dislocation of the hip. Clinical orthopaedics and related research, (377), 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200008000-00012
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2021). Hip dislocation. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/hip-dislocation
Kellam, P., & Ostrum, R. F. (2016). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Avascular Necrosis and Posttraumatic Arthritis After Traumatic Hip Dislocation. Journal of orthopaedic trauma, 30(1), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000419
Ma, H. H., Huang, C. C., Pai, F. Y., Chang, M. C., Chen, W. M., & Huang, T. F. (2020). Long-term results in the patients with traumatic hip fracture-dislocation: Important prognostic factors. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association : JCMA, 83(7), 686–689. https://doi.org/10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000366
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2022). Developmental dislocation (dysplasia) of the hip (DDH). https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/developmental-dislocation-dysplasia-of-the-hip-ddh/
Post Disclaimer *
Professional Scope of Practice *
The information herein on "Hip Dislocation: Causes, Procedures, and Rehabilitation" is not intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional or licensed physician and is not medical advice. We encourage you to make healthcare decisions based on your research and partnership with a qualified healthcare professional.
Blog Information & Scope Discussions
Welcome to El Paso's Premier Fitness, Injury Care Clinic & Wellness Blog, where Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, FNP-C, a Multi-State board-certified Family Practice Nurse Practitioner (FNP-BC) and Chiropractor (DC), presents insights on how our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to holistic healing and personalized care. Our practice aligns with evidence-based treatment protocols inspired by integrative medicine principles, similar to those found on this site and our family practice-based chiromed.com site, focusing on restoring health naturally for patients of all ages.
Our areas of multidisciplinary practice include Wellness & Nutrition, Chronic Pain, Personal Injury, Auto Accident Care, Work Injuries, Back Injury, Low Back Pain, Neck Pain, Migraine Headaches, Sports Injuries, Severe Sciatica, Scoliosis, Complex Herniated Discs, Fibromyalgia, Chronic Pain, Complex Injuries, Stress Management, Functional Medicine Treatments, and in-scope care protocols.
Our information scope is multidisciplinary, focusing on musculoskeletal and physical medicine, wellness, contributing etiological viscerosomatic disturbances within clinical presentations, associated somato-visceral reflex clinical dynamics, subluxation complexes, sensitive health issues, and functional medicine articles, topics, and discussions.
We provide and present clinical collaboration with specialists from various disciplines. Each specialist is governed by their professional scope of practice and their jurisdiction of licensure. We use functional health & wellness protocols to treat and support care for musculoskeletal injuries or disorders.
Our videos, posts, topics, and insights address clinical matters and issues that are directly or indirectly related to our clinical scope of practice.
Our office has made a reasonable effort to provide supportive citations and has identified relevant research studies that support our posts. We provide copies of supporting research studies upon request to regulatory boards and the public.
We understand that we cover matters that require an additional explanation of how they may assist in a particular care plan or treatment protocol; therefore, to discuss the subject matter above further, please feel free to ask Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC, or contact us at 915-850-0900.
We are here to help you and your family.
Blessings
Dr. Alex Jimenez DC, MSACP, APRN, FNP-BC*, CCST, IFMCP, CFMP, ATN
email: [email protected]
Multidisciplinary Licensing & Board Certifications:
Licensed as a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) in Texas & New Mexico*
Texas DC License #: TX5807, Verified: TX5807
New Mexico DC License #: NM-DC2182, Verified: NM-DC2182
Multi-State Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN*) in Texas & Multi-States
Multistate Compact APRN License by Endorsement (42 States)
Texas APRN License #: 1191402, Verified: 1191402 *
Florida APRN License #: 11043890, Verified: APRN11043890 *
Verify Link: Nursys License Verifier
* Prescriptive Authority Authorized
ANCC FNP-BC: Board Certified Nurse Practitioner*
Compact Status: Multi-State License: Authorized to Practice in 40 States*
Graduate with Honors: ICHS: MSN-FNP (Family Nurse Practitioner Program)
Degree Granted. Master's in Family Practice MSN Diploma (Cum Laude)
Dr. Alex Jimenez, DC, APRN, FNP-BC*, CFMP, IFMCP, ATN, CCST
My Digital Business Card
RN: Registered Nurse
APRNP: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
FNP: Family Practice Specialization
DC: Doctor of Chiropractic
CFMP: Certified Functional Medicine Provider
MSN-FNP: Master of Science in Family Practice Medicine
MSACP: Master of Science in Advanced Clinical Practice
IFMCP: Institute of Functional Medicine
CCST: Certified Chiropractic Spinal Trauma
ATN: Advanced Translational Neutrogenomics



